Monthly GST Return filing
Unlock hassle-free GST Returns with our unbeatable plan at just ₹299/month! Simplify your tax process with expert assistance, timely submissions, and zero stress. Don't miss out on this incredible offer—make your GST worries disappear today. Act fast and join the many satisfied customers who have already transformed their tax experience. 
Qurterly GST Return Fililing
Introducing our fantastic quarterly GST Return package for just ₹799! Enjoy three months of seamless GST management with expert support, timely filings, and absolute peace of mind. Save more and stress less with this incredible deal. Upgrade your tax game today and join the ranks of savvy business owners who trust us with their GST returns. 🚀✨ #GSTSimplified #TaxEase #QuarterlySavings
Halfyearly GST Return filing
Discover our unbeatable half-yearly GST filing package for just ₹1499! Get six months of seamless GST management with expert support, on-time filings, and complete peace of mind. This incredible deal offers you significant savings and effortless compliance. Elevate your business efficiency today and join the many who trust us for their GST returns. 🚀✨ #GSTSimplified #TaxEase #HalfYearlySavings


Yearly GST & ITR Return Filing Combo Offer
Unlock ultimate convenience with our exclusive yearly plan at just ₹3999! Enjoy an entire year of seamless GST Return filing and ITR filing, all in one comprehensive package. With expert support, timely submissions, and unbeatable value, this is the perfect solution for your business. Simplify your tax obligations and save big with this incredible offer. Join our satisfied clients and make tax season a breeze! 🚀✨ #GSTSimplified #TaxEase #YearlySavings #AllInOne
What is GST Return?

A GST (Goods and Services Tax) Return is a document that contains details of all income/sales and expenses/purchases which a taxpayer is required to file with the tax administrative authorities. This is used by tax authorities to calculate the net tax liability. Under the GST regime in India, registered dealers have to file GST returns that include:
- Sales and Purchases: Details of outward and inward supplies of goods and services.
- Tax Paid and Collected: The amount of tax payable and paid.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): The credit claimed for the tax paid on purchases.
Types of GST Returns
There are several types of GST returns, each serving a specific purpose. Some of the common ones include:
- GSTR-1: Details of outward supplies of goods and services.
- GSTR-2A/2B: Auto-drafted details of inward supplies (purchases).
- GSTR-3B: Summary return of inward and outward supplies, tax liability, and ITC.
- GSTR-4: Return for composition scheme taxpayers.
- GSTR-9: Annual return for regular taxpayers.
- GSTR-10: Final return for taxpayers whose GST registration has been cancelled or surrendered.
- GSTR-11: Return for taxpayers with a Unique Identification Number (UIN) to get a refund under GST.
GST Filing Process
- Preparation: Gather all required information related to sales, purchases, tax paid, and ITC.
- Logging In: Access the GST portal (https://www.gst.gov.in) using your credentials.
- Filing: Enter details into the appropriate GST return form.
- Submission: Review and submit the return.
- Payment: Pay any tax liability, if applicable.
- Acknowledgement: Receive an acknowledgement receipt from the GST portal.
Importance of Gst Filling
Filing GST returns is crucial because it helps maintain compliance with GST laws and regulations. It also ensures:
- Legal Compliance: Avoid penalties and interest for late or non-filing.
- Claiming ITC: Proper filing is necessary to claim input tax credit on purchases.
- Transparency: Facilitates transparency in the tax system and business operations.
- Government Revenue: Ensures the government receives timely tax revenue.
Regular and accurate filing of GST returns is essential for the smooth functioning of the GST system and for businesses to stay compliant with tax regulations.
Who Should File GST Returns?

Goods and Services Tax (GST) returns need to be filed by various entities involved in the supply of goods and services. The specific requirements for who should file GST returns can vary by jurisdiction, but generally include the following categories:
- Registered Businesses: Any business entity that is registered under the GST system is required to file GST returns. This includes businesses with an annual turnover exceeding the threshold limit set by the respective country's GST laws.
- Casual Taxable Persons: Individuals or businesses that occasionally supply goods or services in a territory where GST is applicable but do not have a fixed place of business in that territory.
- Non-Resident Taxable Persons: Foreign entities that supply goods or services in a territory where GST is applicable but do not have a permanent establishment there.
- Composition Scheme Dealers: Small businesses that opt for the composition scheme, which allows them to pay a fixed percentage of their turnover as tax instead of the standard GST rate, must file returns quarterly.
- Input Service Distributors (ISD): An office of a business that receives tax invoices for input services and distributes the tax credits to other branches of the same business.
- E-Commerce Operators: Entities that provide a platform for other suppliers to sell goods and services must file GST returns, especially regarding the supplies made through their platforms.
- TDS and TCS Registrants: Entities that are required to deduct or collect tax at source (TDS/TCS) under GST laws must file returns showing the amount of tax deducted or collected.
- Voluntary Registrants: Businesses that register for GST voluntarily, even if their turnover is below the threshold limit, are required to file GST returns.
- Persons Making Inter-State Supply: Any person making inter-state supplies of goods or services is required to register for GST and file returns, regardless of the threshold limit.
- Others as Notified: Any other category of persons or entities that the respective tax authority may notify from time to time.
The frequency and type of GST returns (monthly, quarterly, annual) to be filed depend on the nature and turnover of the business. For example, regular taxpayers usually need to file monthly returns, whereas composition scheme dealers file quarterly returns.
It is important to consult with local tax professionals or refer to the specific GST guidelines of the respective country to ensure compliance with all filing requirements.
How Many Returns are there under GST?
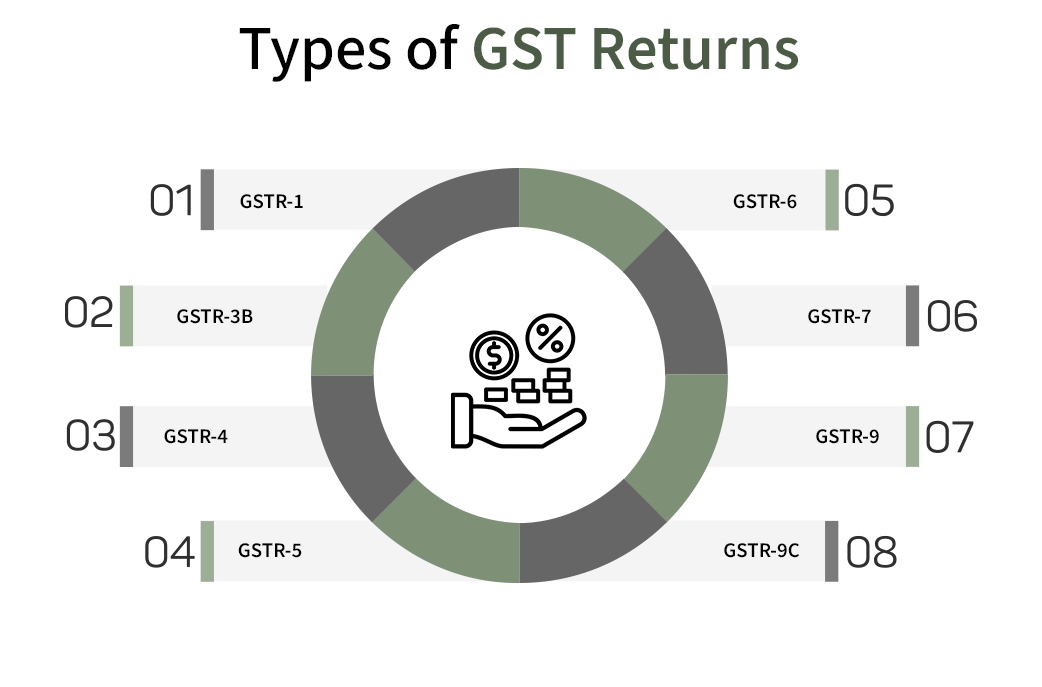
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India, businesses are required to file various types of returns, depending on their nature and activities. Here is a summary of the key GST returns:
- GSTR-1: Monthly return for outward supplies of goods or services. This is filed by the 11th of the subsequent month.
- GSTR-2A: Auto-drafted return for inward supplies made available to the recipient based on GSTR-1 filed by the supplier. This is not to be filed but can be used for reconciliation.
- GSTR-3B: Monthly self-declaration return summarizing the details of outward supplies and input tax credit claimed. This is filed by the 20th of the subsequent month.
- GSTR-4: Quarterly return for composition scheme taxpayers, to be filed by the 18th of the month following the quarter.
- GSTR-5: Monthly return for non-resident taxable persons, to be filed by the 20th of the subsequent month or within 7 days after the expiry of registration.
- GSTR-6: Monthly return for input service distributors (ISD), to be filed by the 13th of the subsequent month.
- GSTR-7: Monthly return for authorities deducting tax at source (TDS), to be filed by the 10th of the subsequent month.
- GSTR-8: Monthly return for e-commerce operators required to collect tax at source (TCS), to be filed by the 10th of the subsequent month.
- GSTR-9: Annual return for regular taxpayers, to be filed by the 31st of December following the end of the financial year.
- GSTR-9A: Annual return for composition scheme taxpayers, to be filed by the 31st of December following the end of the financial year.
- GSTR-9C: Annual audit report for taxpayers with a turnover exceeding ₹2 crores, to be filed along with GSTR-9.
- GSTR-10: Final return to be filed within three months of the cancellation of GST registration.
- GSTR-11: Monthly return for persons with UIN (Unique Identification Number) claiming a refund, to be filed by the 28th of the subsequent month.
Each return has specific requirements and is aimed at ensuring comprehensive compliance with GST regulations, reflecting different aspects of a business's transactions.
Penalty for Late Filing GST Returns

Late filing of GST (Goods and Services Tax) returns in many countries, including India, can result in several penalties and consequences. Here is a detailed look at the penalties for late filing of GST returns:
- Late Fee
A late fee is charged for each day the return is delayed. The amount of the late fee can vary, but as an example, in India, the typical late fees are as follows:
- For GSTR-3B (monthly return):
- For GSTR-1 (outward supplies return):
- Rs. 200 per day of delay (Rs. 100 each for CGST and SGST/UTGST)
- This can be subject to a maximum cap which varies from state to state.
- Interest on Late Payment
If the GST return has any tax liability, interest is charged on the outstanding amount. The interest rate is typically around 18% per annum. The interest is calculated from the due date of the tax until the actual date of payment.
- Restriction on Input Tax Credit
Late filing of GST returns can lead to the restriction or denial of Input Tax Credit (ITC) for the period of delay, affecting the cash flow and working capital of the business.
- Penalty
In addition to the late fee and interest, a penalty may be imposed for deliberate non-compliance or repeated late filing. This penalty can be more severe and may be determined based on the specific circumstances and the amount of tax involved.
- Legal Consequences
Continuous non-filing or late filing can result in legal actions, including the potential for prosecution under GST laws. In extreme cases, it can lead to the suspension or cancellation of GST registration.
- Blocking of e-Way Bill
For businesses involved in the transportation of goods, non-filing of GST returns for a consecutive period (e.g., two months in India) can result in the blocking of e-way bills, which can disrupt the supply chain and business operations.
- Increased Scrutiny and Audits
Habitual late filers may face increased scrutiny and audits from GST authorities, leading to additional compliance costs and potential penalties.
Steps to Mitigate Late Filing Penalties
- Timely Reminders: Set up reminders for GST return filing deadlines.
- Automated Systems: Use GST compliance software to ensure timely filing and payment.
- Professional Help: Consider hiring a tax professional or consultant to manage GST compliance.
- Regular Review: Regularly review GST return filings and payments to ensure they are up to date.
Understanding and adhering to GST return filing deadlines can save businesses from financial penalties and legal issues. It’s crucial to stay informed about the specific regulations and deadlines in your jurisdiction, as they can vary.
