Cloud management refers to the processes and tools utilized for overseeing cloud computing resources and services. It encompasses various tasks to ensure that cloud services are optimized, secure, and efficiently utilized. Here's a comprehensive overview:
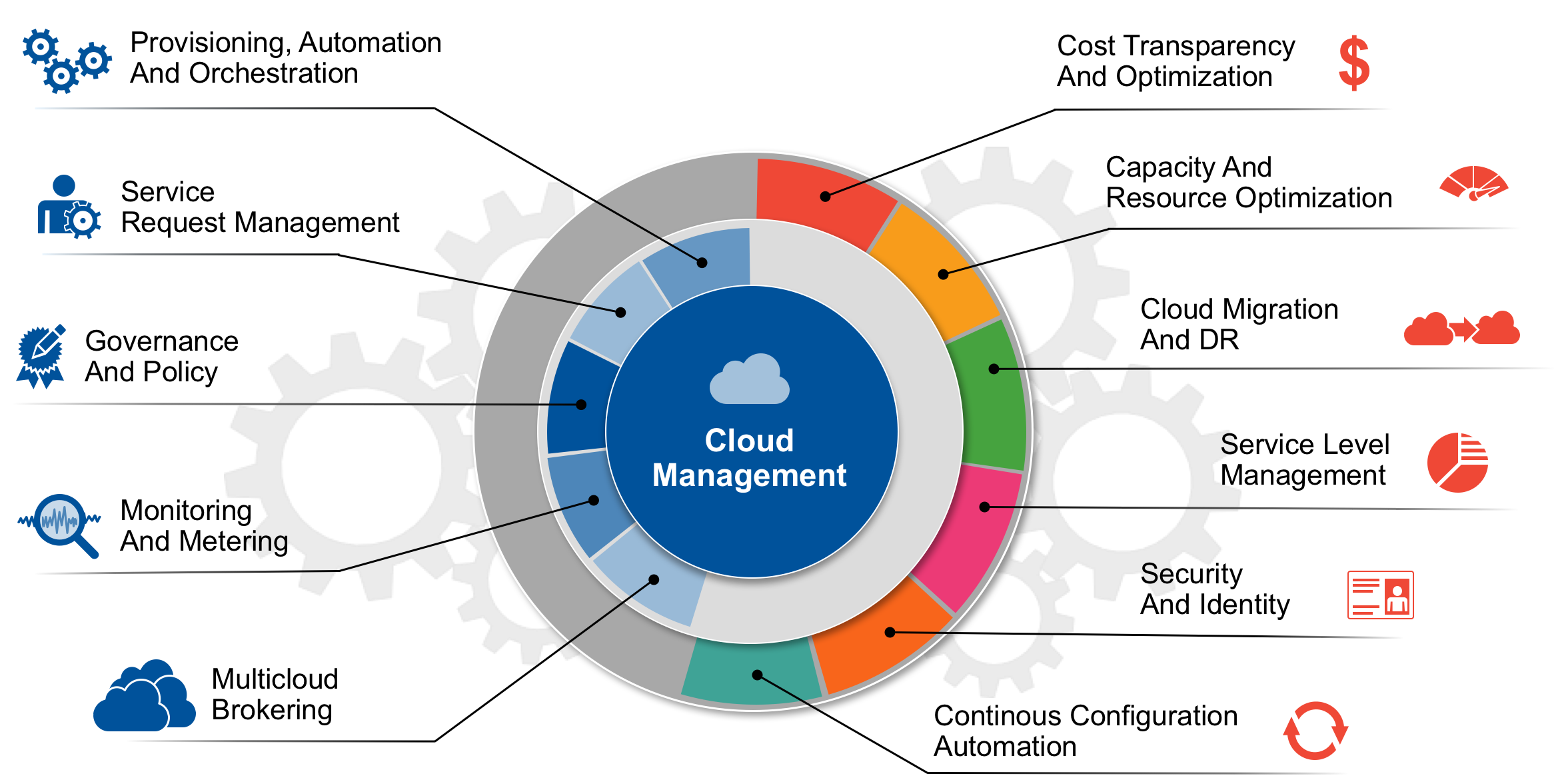
Key Components of Cloud Management
1. Provisioning and Automation:
-
- Provisioning: This involves allocating cloud resources to applications or users. Automated provisioning tools help in dynamically assigning resources based on demand, ensuring efficient usage.
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks such as scaling, backups, and monitoring helps in reducing manual intervention and errors, thereby improving efficiency.
2. Monitoring and Performance Management:
-
- Monitoring: Continuous tracking of cloud resources and applications is critical. Monitoring tools provide real-time insights into the performance, availability, and health of the infrastructure.
- Performance Management: Ensures that applications run optimally. It includes performance tuning, load balancing, and resource optimization to meet the desired service levels.
3. Cost Management and Optimization:
-
- Cost Tracking: Understanding and managing cloud expenses is crucial. Tools for tracking usage and spending help in budgeting and cost forecasting.
- Optimization: Identifying and eliminating wasted resources, such as underutilized virtual machines, to reduce costs.
4. Security and Compliance:
-
- Security: Protecting cloud resources from threats. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, and threat detection mechanisms.
- Compliance: Ensuring that cloud operations adhere to regulatory standards and industry best practices, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others.
5. Data Management:
-
- Data Backup and Recovery: Ensuring data is backed up regularly and can be restored quickly in case of data loss.
- Data Integration: Facilitating the movement and integration of data across different cloud environments and on-premises systems.
6. Service Level Management:
Establishing and maintaining service level agreements (SLAs) with cloud providers to ensure that the agreed-upon performance and availability standards are met.

Tools and Platforms for Cloud Management
1. Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs): Provide a unified interface for managing multiple cloud services and environments. Examples include:
-
- VMware vRealize Suite: A comprehensive platform for managing hybrid cloud environments.
- Microsoft Azure Management Tools: Includes Azure Cost Management, Azure Monitor, and Azure Automation.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Management Tools: Such as AWS CloudFormation, AWS CloudTrail, and AWS Cost Explorer.
3. Third-Party Tools:
-
- RightScale: A multi-cloud management platform offering automation, governance, and analytics.
- CloudHealth: Provides insights into cloud usage, costs, and performance, helping in optimizing cloud operations.
- Datadog: A monitoring and analytics platform for cloud-scale applications.
Best Practices in Cloud Management
- Adopt a Multi-Cloud Strategy: Utilizing multiple cloud providers can prevent vendor lock-in and improve resilience.
- Implement Strong Governance: Establish clear policies and governance frameworks to manage access, security, and compliance.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor usage and performance, and optimize resources to ensure cost-effectiveness.
- Emphasize Security: Implement robust security measures and regular audits to protect cloud resources.
- Train Staff: Ensure that your IT staff is well-versed in cloud technologies and best practices for management.
Challenges in Cloud Management
- Complexity: Managing diverse cloud environments and services can be complex and requires sophisticated tools and skills.
- Security Risks: Protecting data and applications in the cloud involves addressing various security threats.
- Cost Management: Cloud costs can quickly escalate without proper tracking and optimization.
- Compliance: Adhering to different regulatory requirements across various jurisdictions can be challenging.
Conclusion
Effective cloud management is essential for maximizing the benefits of cloud computing. By implementing the right tools, processes, and best practices, organizations can ensure that their cloud resources are secure, cost-effective, and optimally utilized. As cloud technologies continue to evolve, staying abreast of new developments and adapting management strategies accordingly will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.