Core reporting systems: are fundamental tools organisations use to collect, process, analyze, and present data in a coherent and actionable format. These systems are essential for decision-making, strategic planning, compliance, and performance monitoring. This document explores the key components, functionalities, and benefits of core reporting systems, as well as considerations for their implementation.
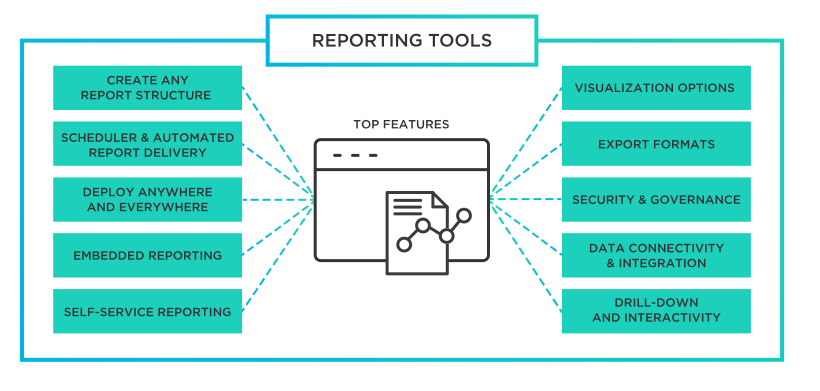
Key Components of Core Reporting Systems
Core reporting systems typically consist of several integral components:
- Data Collection
- Sources: Data can be collected from various sources including databases, external APIs, spreadsheets, and user inputs.
- Methods: Automated data extraction, manual entry, and integration with other systems are common data collection methods.
- Data Processing
- Cleaning: Ensures that the data is accurate, complete, and free of errors.
- Transformation: Converts data into a suitable format for analysis, often involving normalization, aggregation, and enrichment.
- Data Storage
- Databases: Structured storage solutions such as relational databases (e.g., SQL) or NoSQL databases.
- Data Warehouses: Centralized repositories that store large volumes of structured data for reporting and analysis.
- Data Analysis
- Tools: Analytical tools and software like SQL, Python, R, and specialized business intelligence (BI) tools.
- Techniques: Statistical analysis, data mining, machine learning, and predictive analytics.
- Reporting
- Formats: Reports can be generated in various formats including dashboards, visualizations (charts, graphs), and textual summaries.
- Delivery: Reports can be delivered via email, web portals, or integrated into other applications.
- User Interface
- Accessibility: Intuitive interfaces that allow users to interact with the system, create custom reports, and access data insights.
- Customization: User-friendly features that enable customization according to specific user needs and preferences.
Functionalities of Core Reporting Systems
Core reporting systems offer a wide range of functionalities to support organizational needs:
- Real-time Reporting
- Provides up-to-date information allowing for timely decision-making.
- Integrates with live data sources to ensure the latest data is always available.
- Ad-hoc Reporting
- Enables users to create reports on the fly without predefined templates.
- Supports dynamic querying and filtering to address specific questions and requirements.
- Scheduled Reporting
- Automates report generation and distribution at predefined intervals.
- Ensures consistent reporting cycles and reduces manual effort.
- Interactive Dashboards
- Offers visual representations of data through interactive charts and graphs.
- Allows users to drill down into specific data points for deeper insights.
- Compliance Reporting
- Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by providing accurate and timely reports.
- Often includes predefined templates and formats required by regulatory bodies.
Benefits of Core Reporting Systems
Implementing core reporting systems offers numerous benefits to organizations:
- Improved Decision Making
- Provides reliable data and insights to support informed decision-making.
- Reduces the reliance on intuition or guesswork.
- Enhanced Efficiency
- Automates data collection, processing, and reporting, saving time and reducing manual effort.
- Streamlines workflows and reduces redundancy.
- Better Data Management
- Ensures data integrity, consistency, and accuracy through centralized data management.
- Facilitates easy access to historical data for trend analysis.
- Increased Transparency
- Promotes transparency within the organization by making data accessible and understandable.
- Builds trust among stakeholders by providing clear and concise reports.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Helps ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Reduces the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
Considerations for Implementation
Implementing a core reporting system involves several important considerations:
- System Integration
- Ensuring the new system can integrate seamlessly with existing systems and data sources.
- Addressing compatibility issues and data migration challenges.
- Scalability
- Choosing a system that can scale with the organization’s growth and evolving data needs.
- Considering both current requirements and future expansion.
- User Training
- Providing comprehensive training to users to ensure effective use of the system.
- Offering ongoing support and resources to address any issues or questions.
- Cost
- Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including initial setup, maintenance, and potential upgrades.
- Balancing cost with the expected return on investment and benefits.
- Security
- Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and industry standards.
Conclusion
Core reporting systems are vital for modern organizations seeking to harness the power of data. By providing accurate, timely, and actionable insights, these systems support better decision-making, enhance efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance. When selecting and implementing a core reporting system, it is essential to consider factors such as integration, scalability, user training, cost, and security to maximize the benefits and ensure long-term success.