Device-Friendly Website: A device-friendly website, also known as a responsive website, is designed to provide an optimal viewing and interaction experience across a wide range of devices, from desktop computers to smartphones and tablets. This adaptability is crucial in today's digital landscape, where users access the internet through various devices with different screen sizes and capabilities. Here are key aspects of a device-friendly website:

1. Responsive Design
Responsive web design (RWD) ensures that the layout and content of a website adjust seamlessly to different screen sizes and resolutions. This is achieved through flexible grids, layouts, images, and the use of CSS media queries. A responsive design eliminates the need for separate mobile and desktop versions of a site, ensuring consistency in user experience.

2. Mobile-First Approach
A mobile-first approach involves designing the website starting with the smallest screen size and then scaling up. This method prioritizes the mobile user experience, which is essential given that mobile internet usage has surpassed desktop usage. Features such as touch-friendly navigation, simplified content, and fast loading times are crucial in this approach.

3. Fast Load Times
Speed is a critical factor for device-friendly websites. Users expect pages to load quickly, and delays can lead to high bounce rates. Techniques to enhance speed include optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, minimizing HTTP requests, and using content delivery networks (CDNs). Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool can be useful for identifying and addressing speed issues.

4. Easy Navigation
Navigation should be intuitive and accessible on all devices. This includes touch-friendly menus and buttons that are easy to interact with on smaller screens. A clear, consistent navigation structure helps users find information quickly and improves the overall user experience.

5. Readable Text
The text must be legible on all devices without the need for zooming. This involves using appropriate font sizes, line heights, and contrast. Ensuring readability enhances accessibility and user satisfaction.

6. Accessible Design
A device-friendly website must also be accessible to users with disabilities. This includes providing alt text for images, using semantic HTML, ensuring keyboard navigability, and adhering to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Accessibility not only improves user experience but also complies with legal standards in many regions.
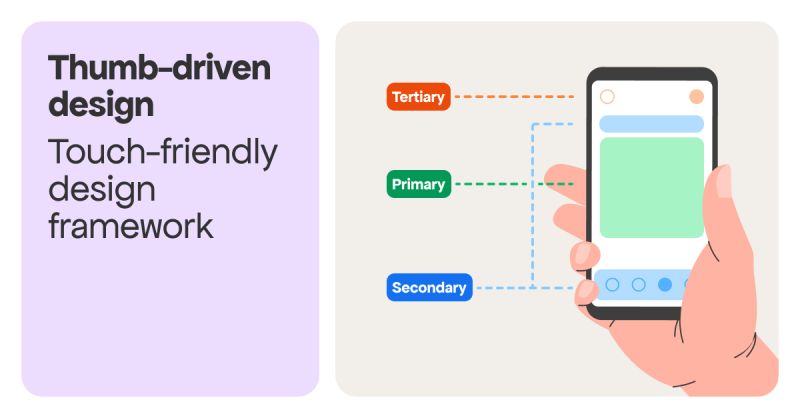
7. Touch-Friendly Elements
Interactive elements such as buttons, links, and forms should be designed with touch screens in mind. This includes ensuring that clickable elements are large enough to tap easily and spaced adequately to prevent accidental clicks.

8. Consistent Experience
Consistency in design and functionality across devices ensures a seamless user experience. Users should be able to switch between devices without confusion or loss of functionality. This consistency builds trust and familiarity with the website.
9. Analytics and Testing
Regularly testing the website on various devices and using analytics to monitor user behaviour can provide insights into areas needing improvement. Tools like Google Analytics, BrowserStack, and real user feedback are invaluable for maintaining and optimizing a device-friendly website.
Conclusion
In an era where users access the web from an array of devices, having a device-friendly website is no longer optional; it’s essential. Implementing responsive design, prioritizing speed, ensuring accessibility, and maintaining consistency is critical to providing a positive user experience. By focusing on these elements, businesses can enhance user satisfaction, reduce bounce rates, and ultimately drive more conversions. Read More... About Another Topic